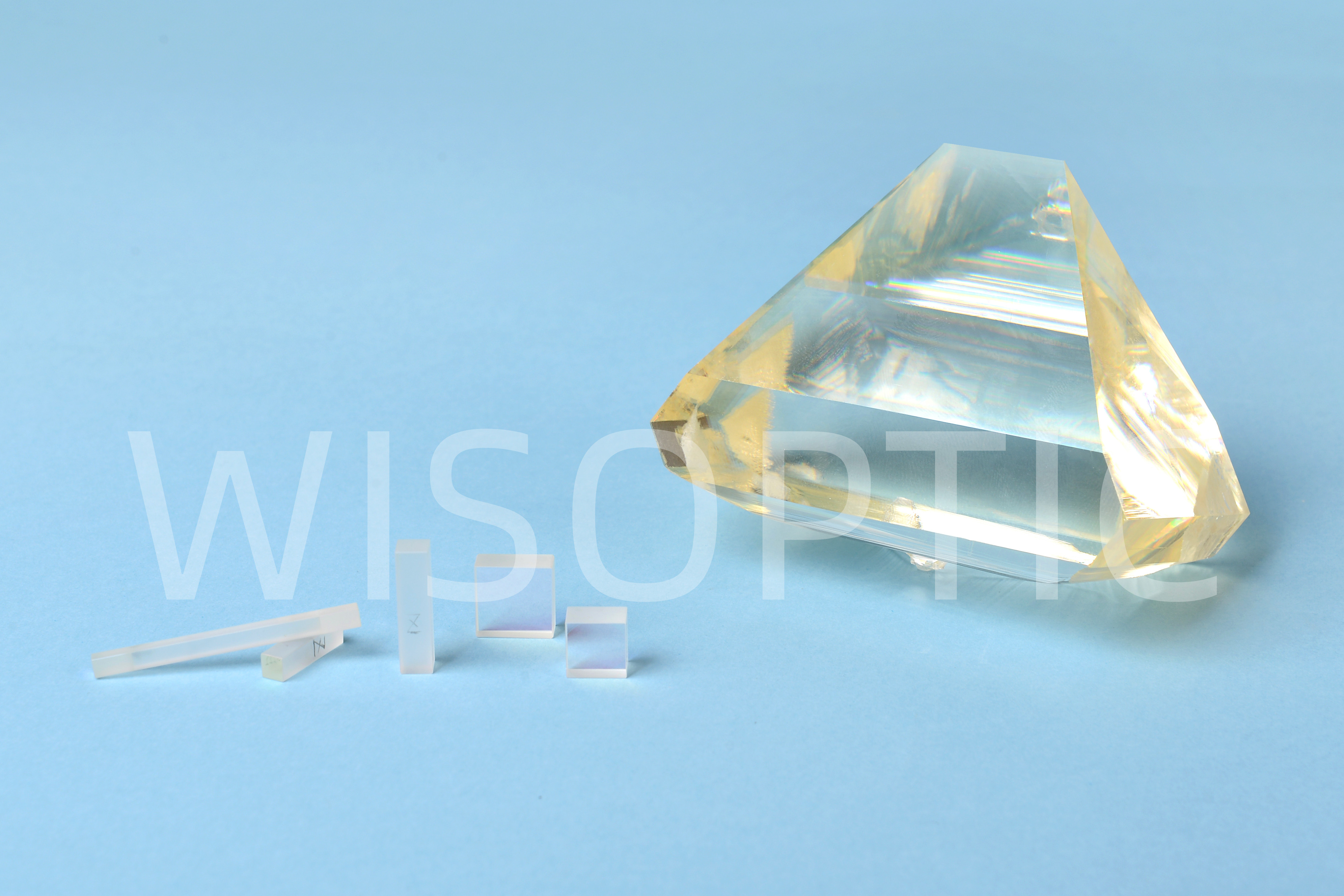
KTP / GTR-KTP Crystal
KTP (KTiOPO4 ) is one of the most commonly used nonlinear optical materials. For example, it’s regularly used for frequency doubling of Nd:YAG lasers and other Nd-doped lasers, particularly at low or medium-power density. KTP is also widely used as OPO, EOM, optical wave-guide material, and in directional couplers.
KTP exhibits a high optical quality, broad transparency range, wide acceptance angle, small walk-off angle, and type I and II non-critical phase-matching (NCPM) in a wide wavelength range. KTP also has relatively high effective SHG coefficient (about 3 times higher than that of KDP) and fairly high optical damage threshold (>500 MW/cm²).
Regular flux-grown KTP crystals suffer from blackening and efficiency breakdown ("grey-track") when used during SHG process of 1064 nm at high average power levels and repetition rates above 1 kHz. For high average-power applications, WISOPTIC offer high grey track resistance (HGTR) KTP crystals grown by hydrothermal method. Such crystals have a lower initial IR absorption and are less affected by green light than regular KTP, thus avoid the problems of harmonic power instabilities, efficiency drops, crystal blackening, and beam distortion.
As one of the major KTP source suppliers in the whole international market, WISOPTIC has high capability of material selection, processing (polishing, coating), mass production, fast delivery and long guarantee period of quality KTP. It is also worth to mention that our price is quite reasonable.
Contact us for the best solution for your application of KTP crystals.
WISOPTIC Advantages - GTR-KTP
Dimensions:As large as 10×10×15mm
Extinction Ratio:>25dB
Optical Transparency Range:500~2500nm
Laser-induced Damage Threshold:>600MW/cm2 @1064nm,10ns,10Hz, AR coated
Insertion Loss:<1.0% @1064nm
Operation Temperature:-40℃~+65℃ (as high as +80℃)
Frequency Range:as high as 4MHz
WISOPTIC Advantages - KTP
• High homogeneity
• Excellent internal quality
• Top quality of surface polishing
• Large block for various size (20x20x40mm3, max length 60mm)
• Large nonlinear coefficient, high conversion efficiency
• Low insertion losses
• Very competitive price
• Mass production, quick delivery
WISOPTIC Standard Specifications* - KTP
| Dimension Tolerance | ± 0.1 mm |
| Angle Tolerance | < ± 0.25° |
| Flatness | < λ/8 @ 632.8 nm |
| Surface Quality | < 10/5 [S/D] |
| Parallelism | < 20” |
| Perpendicularity | ≤ 5' |
| Chamfer | ≤ 0.2 mm @ 45° |
| Transmitted Wavefront Distortion | < λ/8 @ 632.8 nm |
| Clear Aperture | > 90% central area |
| Coating | AR coating: R<0.2% @ 1064nm, R<0.5% @ 532nm [or HR coating, PR coating, upon request ] |
| Laser Damage Threshold | 500 MW/cm2 for 1064nm, 10ns, 10Hz (AR-coated) |
| * Products with special requirement upon request. | |


Main Features - KTP
• Efficient frequency conversion (1064nm SHG conversion efficiency is about 80%)
• Large nonlinear optical coefficients (15 times that of KDP)
• Wide angular bandwidth and small walk-off angle
• Broad temperature and spectral bandwidth
• Moisture free, no decomposition below 900°C, mechanically stable
• Low cost compare with BBO and LBO
• Gray-tracking at high power (regular KTP)
Primary Applications - KTP
• Frequency doubling (SHG) of Nd-doped lasers (particularly at low or medium-power density) for green/red light generation
• Frequency mixing (SFM) of Nd lasers and diode lasers for blue light generation
• Optical parametric sources (OPG, OPA, OPO) for 0.6-4.5µm tunable output
• E-O modulators, optical switches, directional couplers
• Optical waveguide for integrated NLO and E-O devices
Physical Properties - KTP
| Chemical formula | KTiOPO4 |
| Crystal structure | Orthorhombic |
| Point group | mm2 |
| Space group | Pna21 |
| Lattice constants | a=12.814 Å, b=6.404 Å, c=10.616 Å |
| Density | 3.02 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1149 °C |
| Curie temperature | 939 °C |
| Mohs hardness | 5 |
| Thermal expansion coefficients | ax=11×10-6/K, ay=9×10-6/K, az=0.6×10-6/K |
| Hygroscopicity | non-hygroscopic |
Optical Properties - KTP
| Transparency region (at “0” transmittance level) |
350-4500 nm | ||||
| Refractive indices | nx | ny | nz | ||
| 1064 nm | 1.7386 | 1.7473 | 1.8282 | ||
| 532 nm | 1.7780 | 1.7875 | 1.8875 | ||
| Linear absorption coefficients (@ 1064 nm) |
α < 0.01 / cm | ||||
|
NLO coefficients (@1064nm) |
d31=1.4 pm/V, d32=2.65 pm/V, d33=10.7 pm/V | ||||
|
Electro-optic coefficients |
Low frequency |
High frequency | |||
| r13 | 9.5 pm/V | 8.8 pm/V | |||
| r23 | 15.7 pm/V | 13.8 pm/V | |||
| r33 | 36.3 pm/V | 35.0 pm/V | |||
| r42 | 9.3 pm/V | 8.8 pm/V | |||
| r51 | 7.3 pm/V | 6.9 pm/V | |||
| Phase matching range for: | |||||
| Type 2 SHG in x-y plane | 0.99÷1.08 μm | ||||
| Type 2 SHG in x-z plane | 1.1÷3.4 μm | ||||
| Type 2, SHG@1064 nm, cut angle θ=90°, φ=23.5° | |||||
| Walk-off angle | 4 mrad | ||||
| Angular acceptances | Δθ=55 mrad·cm, Δφ=10 mrad·cm | ||||
| Thermal acceptance | ΔT=22 K·cm | ||||
| Spectral acceptance | Δν=0.56 nm·cm | ||||
| SHG conversion efficiency | 60~77% | ||||











