3. Single pulse energy of E-O Q-switched laser
High repetition frequency and narrow pulse width laser output can be achieved by single laser rod E-O Q-switched oscillator. However, the single pulse energy of such oscillators is usually low, which limits its application in many fields. The design of two series-connected laser rods in the oscillator can improve the single pulse energy. In addition, the MOPA (Master Oscillator Power Amplifier) set outside the laser cavity is also helpful to increase the single pulse energy.
3.1 Technique of dual rods
The refractive index gradient of laser crystal caused by thermal effect will seriously affect the laser mode distribution and reduce the output energy. In order to obtain output with high repetition rate, high gain and fundamental transverse mode, the thermal effect of laser crystal under high pump energy must be avoided. In order to reduce the thermal effect and the gradient change of the refractive index in the laser crystal and increase the output energy, a combination of multiple laser crystals is often used in the resonator, especially the combination of two laser rods. Compared with the single rod design, the dual rod design can also extend the range of the stable zone under the same pumping condition.
In 2014, some researchers adopted the design of series-connected dual rods to make 100 W laser with repetition frequency 10 kHz, pulse width 5 ns, and single pulse energy 24 mJ. In this laser system, two identical Nd:YAG (www.wisoptic.com) rods were side-pumped by LD, and one LN Pockels cell acted as the Q-switching unit.
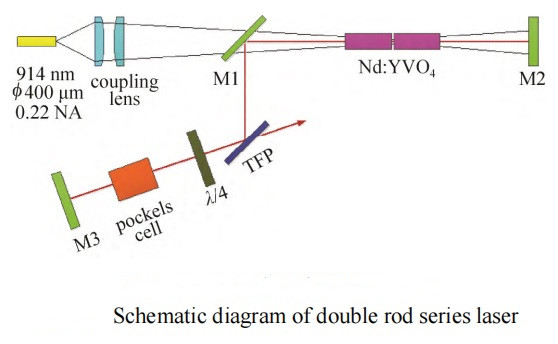
In 2018, someone used 914 nm light with low absorption coefficient to pump two series-connected Nd:YVO4 crystals to improve the thermal stability of the laser system. Stable pulse laser output with pulse width 5 ns and single pulse energy 5 mJ was obtained by using a BBO E-O Q-switch (repetition frequency 7 kHz, www.wisoptic.com). The diagram of this design is shown in the figure below.
Post time: Dec-04-2022